Although it is a focus topic for the majority of organizations, mainly pilot projects were realized or plans for their implementation were developed. [1] An integrated approach, covering the structural changes as well as the functional implementation, is lacking. Hence, the much-anticipated impacts of the transformation remain below expectations. To be successful, it is crucial to reach an equally distributed maturity across the entire organization as well as to start the right initiatives depending on the current maturity level and identified improvement opportunities.
Thus, the question that arises is how to assess a holistic Industry 4.0 readiness?
The journey towards Industry 4.0 is driven by a vision or a target area, expected impacts, functional requirements, and processual ambitions. The interaction of these influencing factors contributes to the success of a transition towards Industry 4.0 – perhaps with a focus on one of the areas smart factory, smart supply chains, smart solutions and smart innovations. In a collaboration with the MIT Center for Digital Business, Capgemini studied nearly 400 companies on how they react to technological opportunities. The digital maturity is represented by the “what” and the “how”- the two areas driving digital transformation, see figure 1. Companies that are mature in both yield business value from implementing Industry 4.0.[2]
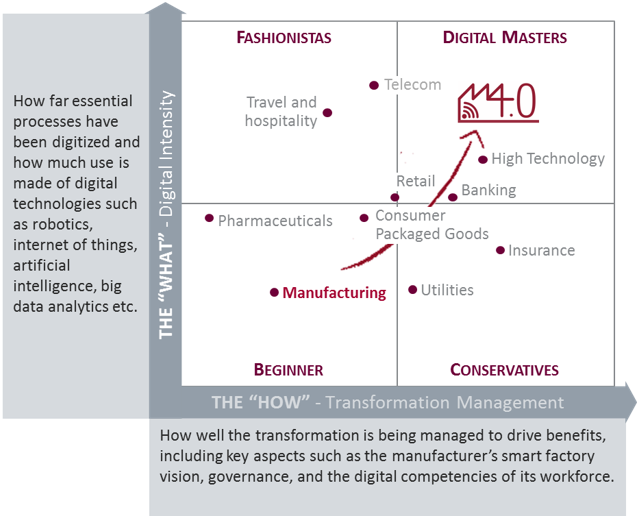
Figure 1: Digital Maturity Matrix by Industry. [3][4]
Focusing on the manufacturing industry, only 12% truly leveraging the power of digital technologies – thus respective companies collectively are in the “Beginners” category. Since a comprehensive maturity assessment is the first step to achieve operational excellence through digital transformation, we specified the Digital Maturity Model towards an Industry 4.0 Maturity Model to gain comparable and tangible insights, see figure 2. [4] Therefore, typical questions concerning the company’s current situation include defining the course of action over the next few years, identifying which organizational changes are needed, which applications are already implemented – and which are missing, and how they operate within the company have to be answered. We defined dimensions to enable a structured study of these aspects describing a company’s Industry 4.0 maturity. The following paragraphs refer to the dimensions by addressing the following questions.
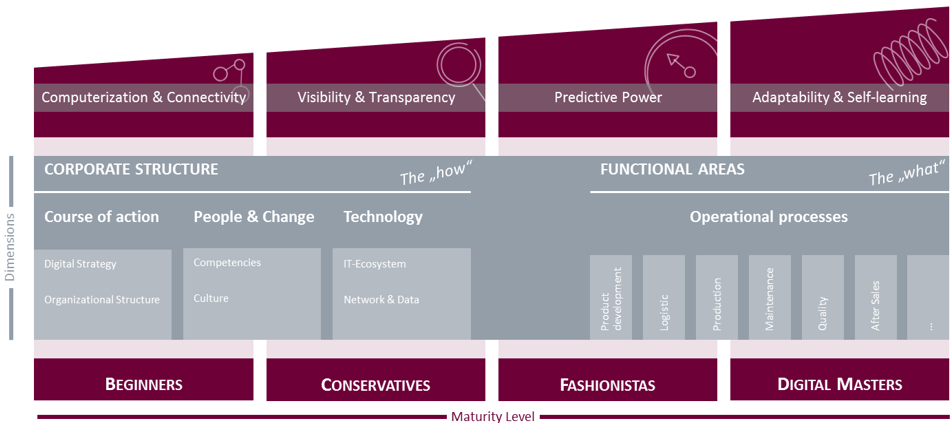
Figure 2: Approaching an Industry 4.0 Maturity Model
Course of action: Is the transformation driven by management ambitions and facilitated by a digital operating model?
A course of action on how to approach the objective of a digital transition provides the necessary guidance and demonstrates the vision of the management. To generate benefits out of the transformation, the operating model of a company has to be transformed to the digital capabilities a company wants to achieve and provide to their employees and customers. This will result in aligned initiatives with the strategy and coordinated resources.
The application of innovative technologies and concepts changes today’s work environment. New responsibilities emerge, requiring both different skill sets and the willingness to interact with smart work places. It is intended that employees contribute proactively with their own ideas instead of just accepting change. If they become part of the change process, the digital journey is off to a flying start.
Technology: Does a governance model ensure an ideal technology ecosystem for enhancing the business performance?
Information and operational technology are inevitably connected with today’s business operations. Obsolete equipment slows down the digital journey. This emphasizes the importance of an adequate governance preparing the IT-architecture for the future.
Operational processes: Are the processes lean and supported efficiently by the technology ecosystem?
To supplement processes with innovative technology, a lean design is a prerequisite. Only a digitalization of lean processes will bring the expected benefits. As part of the continuous improvement, digital solutions are considered to increase the levels of automation and autonomous adaptability in the processes.
The evaluation of answers to these questions defines a frame for a company’s digital journey from a “Beginner” towards a “Digital Master”. How to address the respective dimensions within an organization will be examined in future blog articles.
However, to grow towards a higher maturity level, the necessary technical capabilities have to be acquired additionally. The idea of Industry 4.0 describes a network of autonomous, self-configuring production objects reacting based on their environment and knowledge. [5] key aspect to reach such a production landscape is data collection, analysis and usage. Thus, at the beginning the basic requirements for gathering information have to be implemented to successively build necessary capabilities and realize an intelligent production.
Capability stage: Computerization & Connectivity
Computerization encompasses the deployment of information technologies. This does not imply that all machines are equipped with a digital interface but rather that relevant processes are digitally supported. By replacing the isolated usage with connected business applications, a shift to embedded systems is facilitated.[6]
Capability stage: Visibility & Transparency
Recording events from several data points beyond individual areas in real-time increases the visibility based on information availability and quality. By aggregating this information and a corresponding contextualization, transparency is increased and fast decision making is enabled.[6]
Capability stage: Predictive Power
Deploying the data to anticipate the future based on the likelihood of various scenarios facilitates alerts. Unexpected events can be prevented before they occur. Such a projection increases the decision quality since appropriate measures can be implemented in a time-sensitive manner.[6]
Capability stage: Adaptability & Self-Learning
Improving timely decisions based on data enables the organization to take corresponding measures autonomously. The delegation of decisions allows a rapid adaption to a changing business environment. Based on past reactions on certain events and their respective outcomes, the systems learn and further improve decision-making in the future.[6]
An assessment according to those stages determines which developments a company has to undergo to fruitfully introduce and enhance Industry 4.0. Embedding those degrees in the digital journey, the organizational view is accompanied by technical capabilities. Together, both result in comprehensive maturity levels.
For instance, imagine an organization with a digital strategy and an implemented operating model, whose members feel comfortable with digital information flows. Furthermore, processes are efficient due to an integrated technology ecosystem and the organization operates based on predictions and autonomous adaptations. Therefore, the maturity level “Digital Master” is reached.
Of course, there is no single correct model to assess the digital readiness. With the introduced model, the gap between technical and organizational maturity is closed. By addressing the two dimensions -corporate structure and functional areas – a combined approach for the full picture of an organization’s shape is provided. Assessing the current state and subsequently breaking down those dimensions indicates specific areas requiring action to achieve a common maturity level. Furthermore, the selection of adequate use cases deploying recent technologies is facilitated. Thus, the Industry 4.0 Maturity Model functions as practical guidance for shaping the digital journey.
[1] bitkom research. Industrie 4.0: Status Quo und Perspektiven, 2017
[2] MIT Center for Digital Business, George Westerman, Didier Bonnet and Andrew McAfee. The Advantages of Digital Maturity, 2012
[3] Capgemini Consulting. Smart Factories: How can manufacturers realize the potential of digital industrial revolution, 2017
[4] Capgemini Consulting. Operational Excellence through Digital in Manufacturing Industries, 2013
[5] Forschungsunion und acatech. Umsetzungsempfehlungen für das Zukunftsprojekt Industrie 4.0, 2013
[6] acatech. Industrie 4.0 maturity index. Managing the Digital Transformation of Companies, 2017





































